Modbus Application Overview
This section describes how to build an application for the HCC2 from the example source code using Modbus as the integration mechanism1. This procedure assumes that the sample code is downloaded and installed as described in this section. The high-level architecture of the app created with the sample code is presented below.
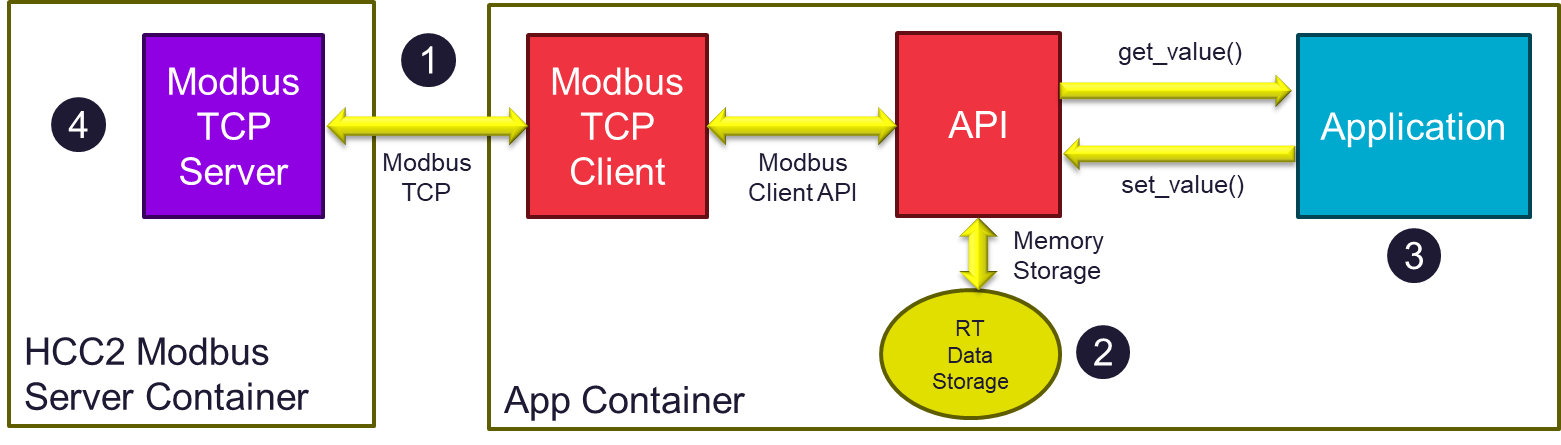
The application structure is based on the following building blocks (see corresponding numbers above):
-
The application includes a Modbus TCP Client. This client periodically scans data and issues writebacks to a Modbus Server available as part of the HCC2 core software.
-
Scanned data are stored in a real-time memory storage that is also part of the application. Likewise, data written to the memory storage are written back to the HCC2 Modbus Server.
-
The application has access to read/write data from/to the memory storage using these API methods:
- For Python
get_value(tag_name) - gets the last scanned value of tag_name (where 'tag' implies a 'data point') set_value(tag_name, value) - sets (writeback) a value on that tag_name. - For C#
GetValue(tag_name) - gets the last scanned value of tag_name. SetValue(tag_name, value) - sets (writeback) a value on that tag_name.
- For Python
-
The HCC2 Modbus Server must be properly configured to accept queries and writebacks from the application.
The following sections will describe each one of the above steps.
-
It is not intended to limit the use of other approaches or methodologies. For instance, you can request data from the Modbus server on demand if this approach is more appropriate for your app behavior. ↩