Managing Data Points
Overview
The following section details how to use a template to create and manage data points in code rather than using App Config Editor or REST Server as mentioned in the Example Application. For more details about data points, refer to the Data Points Overview.
Adding Dynamic Data Points
To add general or configuration data points, call the add_general or add_config method of the DataPoints class.
All data classes, such as GeneralDataPoint and ConfigDataPoint, are found within [api/hcc2_rest_schema.py]
Info
All general and configuration data points must be added before registration.
For more examples, see [examples/define_general_datapoints.py] and [examples/define_config_datapoints.py].
from utils import DataPoints
from api.hcc2_rest_schema import (
TagMetadata, TagUnityUI,
GeneralDataPoint, ConfigDataPoint
)
# Add General Data Point : Int32 Input
DataPoints.add_general(
GeneralDataPoint(
tagSubClass=TagSubClass.PRODUCTION,
topic="inputs.int32In",
metadata=TagMetadata(
dataType=TagDataType.INT32,
unit=UnitType.NONE,
isInput="true",
isOutput="false"
),
unityUI=TagUnityUI(
displayName="Int32 Input",
shortDisplayName="int32In",
uiSize="3"
)
)
)
# Add Config Data Point : Current Limit
DataPoints.add_config(
ConfigDataPoint(
topic="currentLimit",
defaultValue="1.0",
metadata=TagMetadata(
dataType=TagDataType.FLOAT,
unit=UnitType.CURRENT
),
unityUI=TagUnityUI(
displayName="Current Limit",
shortDisplayName="currLimit",
uiSize="3"
)
)
)
Accessing General Data Points
General data points defined either dynamically or statically are available in the DataPoint class to access.
This is most useful for accesssing the fully qualified tag name, which is required for reading and writing to/from data points.
An example of a dynamically defined data point:
DataPoints.add_general(
GeneralDataPoint(
tagSubClass=TagSubClass.PRODUCTION,
topic="inputs.int32In",
metadata=TagMetadata(
dataType=TagDataType.INT32,
unit=UnitType.NONE,
isInput="true",
isOutput="false"
),
unityUI=TagUnityUI(
displayName="Int32 Input",
shortDisplayName="int32In",
uiSize="3"
)
)
)
An example of a statically defined data point within ACE:
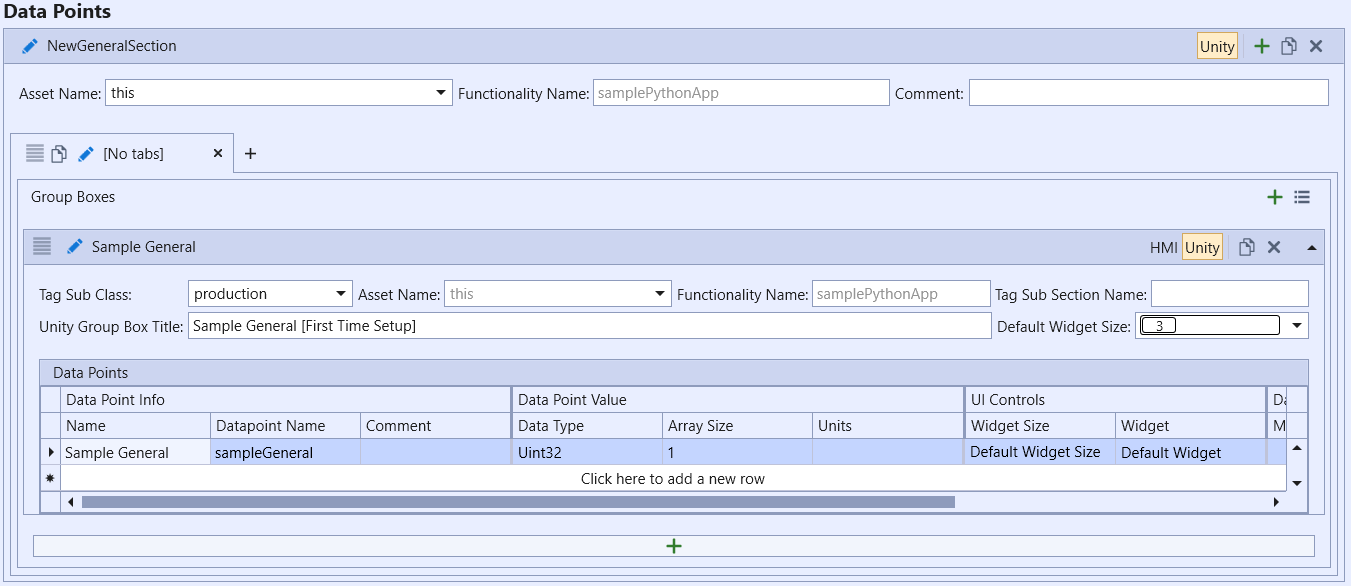
Assuming static_enabled and dynamic_general_enable are enabled and targz is a valid TAR.GZ configuration file within [config.json], then both the dynamic and static registers can be accessed through the DataPoints class.
from utils import DataPoints
# Access general tags fully qualified tag from either the .fqn attribute or resolving the class instance as a string.
# Dynamic Register (By Topic) (periods replaced with underscores, ie inputs.int32In -> inputs_int32In
print(DataPoints.general.inputs_int32In)
print(DataPoints.general.inputs_int32In.fqn)
# Static Registers (By Datapoint Name)
print(DataPoints.general.sampleGeneral)
print(DataPoints.general.sampleGeneral.fqn)
Reading And Writing General Data Points
Read and write values to your general data points by accessing the general tags FQN from the DataPoints class.
Info
For more examples, see [examples\send_read_message.py] and [examples\send_write_message.py].
Reading General Data Points
from utils import DataPoints
from api import RestAPI
rest_api = RestAPI()
# Read the general data point value
messages = rest_api.rest_api.message_read_simple([
# Share a list of FQN accessable from the DataPoints class
DataPoints.general.inputs_int32In.fqn,
DataPoints.general.sampleGeneral.fqn
])
# Print out the read results
print(f"inputs_int32In : {messages[0].value}")
print(f"sampleGeneral : {messages[1].value}")
Writing General Data Points
from utils import DataPoints
from api import RestAPI, SimpleMessage
# Create simple messages
simple_msg_1 = SimpleMessage(DataPoints.general.inputs_int32In.fqn, 800)
simple_msg_2 = SimpleMessage(DataPoints.general.sampleGeneral.fqn, 30000)
# Send write request (List of SimpleMessages)
response = rest_api.message_write_simple([
# Add Simple Messages
simple_msg_1,
simple_msg_2
])
# Check response
if response.ok:
print("All message written!")