Workflow
This section describes the various workflows that an application should implement. These workflows are crucial to take full benefit of the HCC2 echo system.
This section also outlines which APIs are to be used for each workflow.
There are two workflow classifications: simple & advanced. Select a workflow based on your app's nature.
Simple Application (preferred)
- App configuration parameters are atomic or individual in nature.
- Validation of the configuration parameter can be done standalone via validator.js (ACE).
- There is no file in the configuration.
Advanced Application
- App configuration parameters are complex.
- The configuration parameters cannot be validated standalone; the app needs to validate them.
- There is a file in the configuration.
Simple Startup
The app follows this workflow at every startup.
- Register the app.
UsePOST/api/v1/app-registration/{appName}.
Select pre-created tarball for registration.
SelectisComplexProvisionedasfalse. - Send heartbeat false every 10 seconds.
UsePUT/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
SetisUpasfalse. - Read the provisioning status.
UseGET/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
CheckhasNewConfigin the response. If thehasNewConfigistrue, the app was provisioned (configured by user) in the previous cycle. - If the
hasNewConfigistrue- Read all the required data points latest values.
UsePOST/api/v1/message/readorPOST/api/v1/message/read-advanced. - Acknowledge the configuration read.
UsePOST/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}. - Start sending heartbeat true every 30 seconds.
UsePUT/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
SetisUpastrue. - Continue to the business logic of the app.
- Read all the required data points latest values.
- If the
hasNewConfigisfalse- Wait in the Idle loop to be configured.
- In Idle loop keep checking the Simple Reconfiguration/Deployment workflow.
- Do not start the business logic until user configures the app.
Exception
If the app has no configuration parameters, it can start its business logic loop even when hasNewConfig is false.
Example Simple Startup Sequence
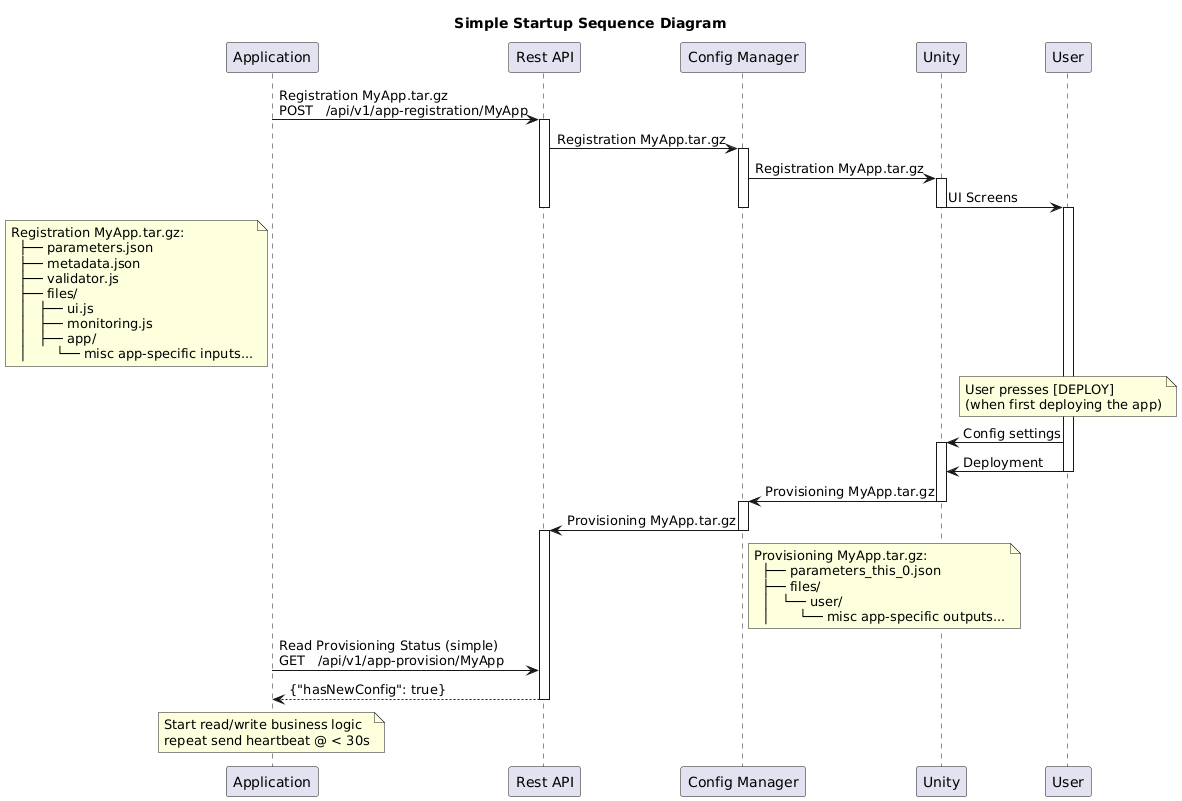
Simple Reconfiguration/Deployment
This workflow allows the app to be reconfigured at runtime. This is a response of the app when a user configures the app on the Unity Edge screen and clicks the deploy button.
The follow logic will be executed continuously, either in the application main loop or in another thread, depending on your implementation.
- Read the provisioning status.
UseGET/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
CheckhasNewConfigin the response.
If thehasNewConfigistrue, a new configuration is deployed from Unity Edge. - If the
hasNewConfigistrue- Read all the required data-point's latest values.
UsePOST/api/v1/message/readorPOST/api/v1/message/read-advanced. - Acknowledge the configuration read.
UsePOST/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
SetisValidastrue. - If the app is in Idle loop, it can start performing the business logic.
- Read all the required data-point's latest values.
- if the
hasNewConfigisfalse- Do nothing.
Advanced Startup
The app follows this workflow at every startup.
- Register the app.
UsePOST/api/v1/app-registration/{appName}.
Select pre-created tarball for registration.
SelectisComplexProvisionedastrue. - Send heartbeat false every 10 seconds.
UsePUT/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
SetisUpasfalse. - Read the provisioning status.
UseGET/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
CheckhasNewConfigin the response. If thehasNewConfigistrue, the app was provisioned (configured by user) in the previous cycle. - If the the
hasNewConfigistrue- Retrieve the tarball of user configuration.
Use
GET/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}/targz. - Extract the tarball and read the user configuration.
- Validate the configuration and send acknowledgement true or false based on the validation result.
UsePOST/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}. - Start sending heartbeat true every 30 seconds.
UsePUT/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
SetisUpastrue. - Continue to the business logic of the App.
- Retrieve the tarball of user configuration.
Use
- If the
hasNewConfigisfalse- Wait in the Idle loop to be configured.
- In Idle loop keep checking the Advanced Reconfiguration/Deployment workflow.
- Do not start the business logic until the user configures the app.
Advanced Reconfiguration/Deployment
This workflow allows the app to be reconfigured at runtime. This is a response of the app when a user configures the app on the Unity Edge screen and clicks the deploy button.
The follow logic will be executed continuously, either in the application main loop or in another thread, depending on your implementation.
- Read the provisioning status.
UseGET/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
CheckhasNewConfigin the response.
If thehasNewConfigistrue, a new configuration is deployed from Unity Edge. - If the the
hasNewConfigistrue- Retrieve the tarball of user configuration.
Use
GET/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}/targz. - Extract the tarball and read the user configuration.
- Validate the configuration and send acknowledgement true or false based on the validation result.
UsePOST/api/v1/app-provision/{appName}.
SetisValidastrueorfalse. - If the application is in Idle loop, it can start performing the business logic
- Retrieve the tarball of user configuration.
Use
- If the
hasNewConfigisfalse- Do nothing.